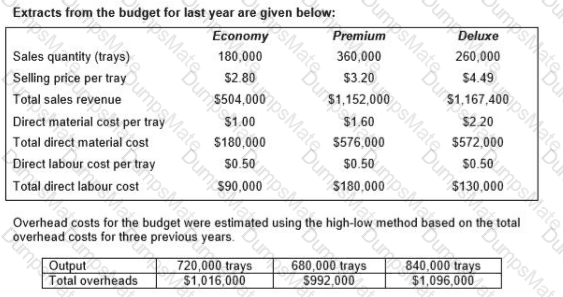
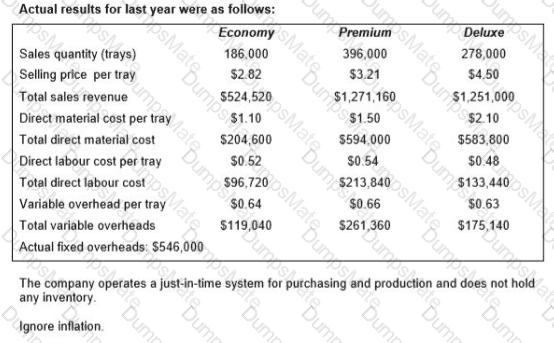
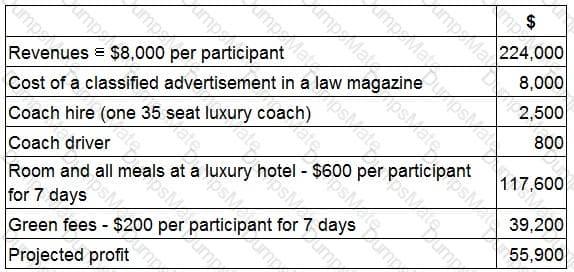
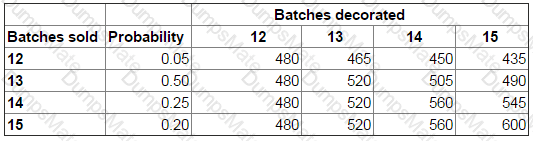
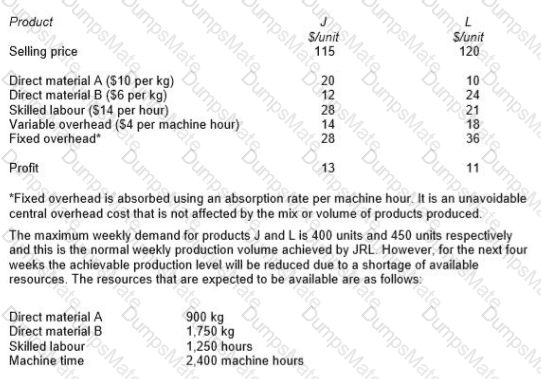
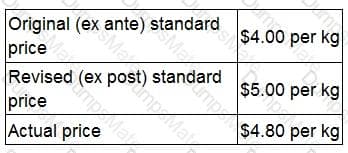
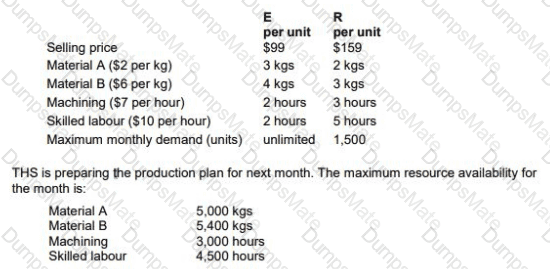
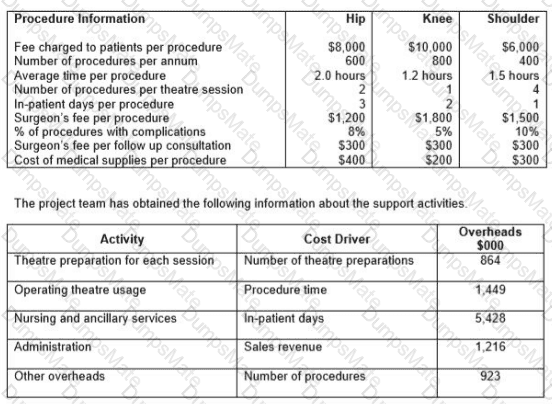
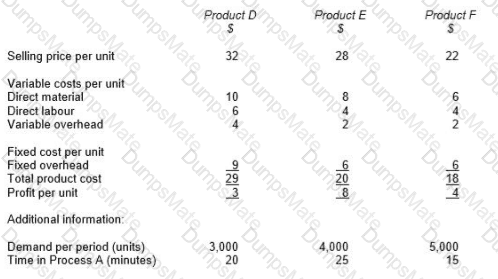
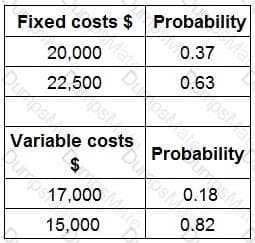
RT produces two products from different quantities of the same resources using a just-in-time (JIT) production system. The selling price and resource requirements of each of the products are shown below:

Market research shows that the maximum demand for products R and T during June 2010 is 500 units and 800 units respectively. This does not include an order that RT has agreed with a commercial customer for the supply of 250 units of R and 350 units of T at selling prices of $100 and $135 per unit respectively. Although the customer will accept part of the order, failure by RT to deliver the order in full by the end of June will cause RT to incur a $10,000 financial penalty. At a recent meeting of the purchasing and production managers to discuss the production plans of RT for June, the following resource restrictions for June were identified: Direct labour hours 7,500 hours
Material A 8,500 kgs
Material B 3,000 litres
Machine hours 7,500 hours
(Refer to previous 2 questions.)
You have now presented your optimum production plan to the purchasing and production managers of RT. During your presentation it became clear that the predicted resource restrictions were rather optimistic. In fact, the managers agreed that the availability of all of the resources could be as much as 10% lower than their original predictions.
Assuming that RT completes the order with the commercial customer, and using linear programming, show the optimum production plan for RT for June 2010 on the basis that the availability of all resources is 10% lower than originally predicted.