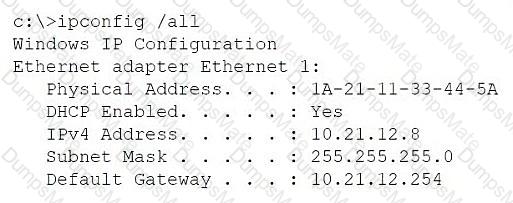
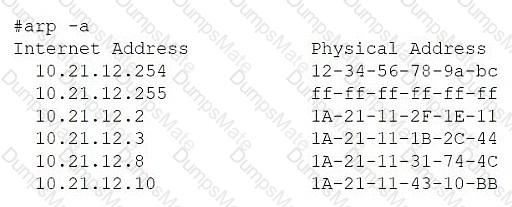
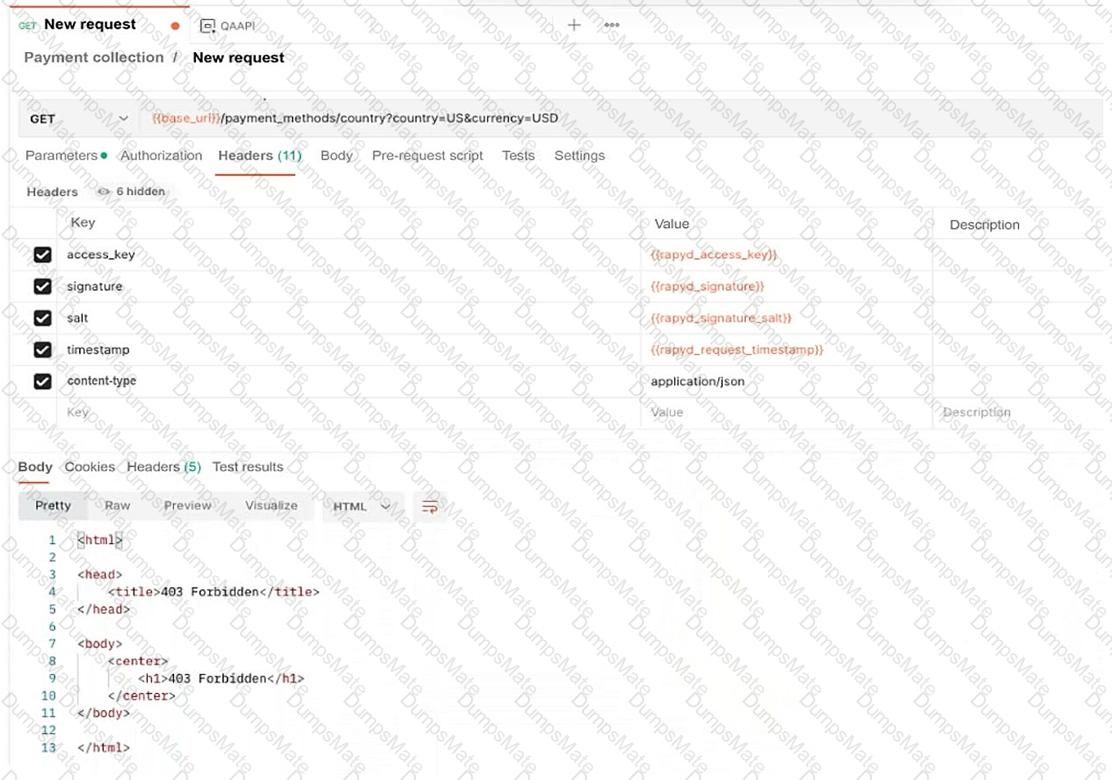
BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) is a wireless personal area network (WPAN) technology designed for applications that require lower energy consumption and reduced cost while maintaining a communication range similar to classic Bluetooth. BLE supportslocation tracking with an accuracy range typically between 1 to 2 meters (approximately 3 to 6 feet), making it ideal for applications that demandfine-grained location services, such as stadium services requiring real-time user proximity data.
According to theCompTIA CloudNetX CNX-001 Official Objectives, under theNetwork Architecture domain, specifically in the subdomain:
"Wireless Technologies: Identify capabilities of BLE, NFC, RFID, and IoT devices within a network environment,"it is outlined that:
"BLE enables proximity-based services and real-time indoor location tracking with high accuracy when used with beacon infrastructure."
"BLE beacons can be deployed throughout a physical space, transmitting signals received by mobile applications to determine a user’s location within a few feet."
"BLE is widely adopted for use cases including indoor navigation, asset tracking, and personalized user engagement, making it a critical technology for modern high-density venues such as stadiums."
In comparison:
SSIDmerely identifies a wireless network and has no location tracking function.
NFCrequires close contact (under 4 cm), and is not suitable for continuous or broad-range tracking.
IoTis an overarching category that includes connected devices and sensors; however, IoT is not a standalone location tracking technology. It may include BLE as a component, butBLE specifically provides the precise location tracking functionality.
These distinctions are explicitly addressed in theCompTIA CloudNetX CNX-001 Study Guide, under the section:
“Emerging Network Technologies and Architectures”, where BLE is described as a key enabling technology for context-aware and location-based services in enterprise and public environments.