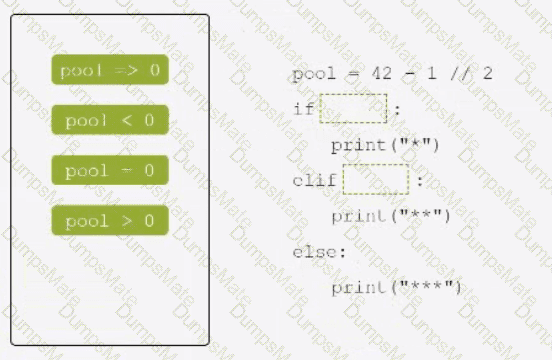
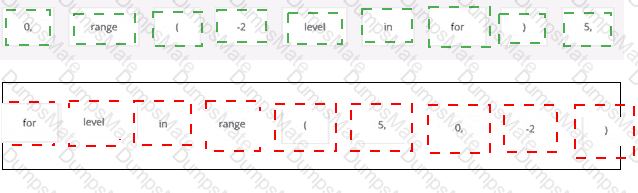
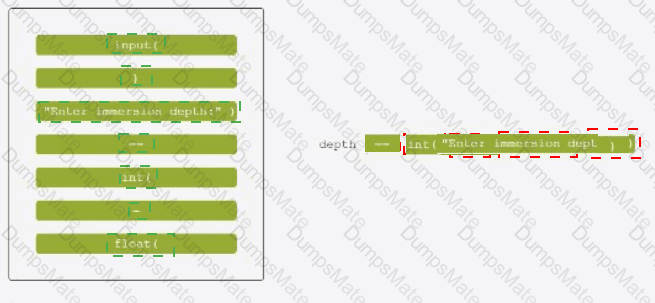
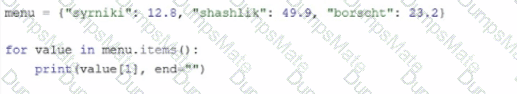The code snippet that you have sent is trying to print the combined length of two lists, “collection” and “duplicate”. The code is as follows:
collection = [] collection.append(1) collection.insert(0, 2) duplicate = collection duplicate.append(3) print(len(collection) + len(duplicate))
The code starts with creating an empty list called “collection” and appending the number 1 to it. The list now contains [1]. Then, the code inserts the number 2 at the beginning of the list. The list now contains [2, 1]. Then, the code creates a new list called “duplicate” and assigns it the value of “collection”. However, this does not create a copy of the list, but rather a reference to the same list object. Therefore, any changes made to “duplicate” will also affect “collection”, and vice versa. Then, the code appends the number 3 to “duplicate”. The list now contains [2, 1, 3], and so does “collection”. Finally, the code tries to print the sum of the lengths of “collection” and “duplicate”. However, this causes an exception, because the len function expects a single argument, not two. The code does not handle the exception, and therefore outputs nothing.
The expected output of the code is nothing, because the code raises an exception and terminates. Therefore, the correct answer is D. The code raises an exception and outputs nothing.